By Ellie Yu, Gassimu Diallo, Miltiadis Vitsas and Anastasia Deligianni
As our world grapples with the pressing need to combat climate change and protect the environment, innovative approaches are emerging to make our infrastructure more sustainable. In the Netherlands, a nation known for its commitment to environmental preservation, remarkable strides have been made in creating greener roadways. These initiatives not only prioritize efficient transportation but also strive to safeguard the natural world they traverse.
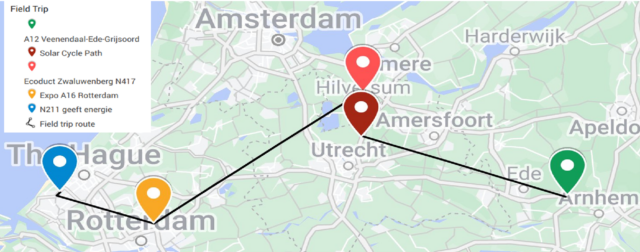
In this blog, we embark on a virtual field visit to some of the pioneering green road projects in the Netherlands. These projects not only showcase the country’s dedication to eco-conscious development but also offer a blueprint for a greener future. From wildlife passages to solar-powered roadways, each initiative is a testament to the harmonious coexistence of infrastructure and nature.
- A12 Veenendaal-Ede-Grijsoord: A Road Through the Wilderness
The A12 Veenendaal-Ede-Grijsoord project, spanning from 2014 to 2032, seeks to address a critical transportation bottleneck while traversing the Veluwe, one of Europe’s largest lowland nature areas. This project demonstrates the Netherlands’ commitment to preserving international environmental values while collaborating with ecological consultancies and research foundations. Some exemplary green measures implemented on this road to safeguard the surrounding natural environment include:
- Reptile passages are under viaduct N224 or beside the N224 north cycle tunnel.
- Rope bridges for pine martens are connected to traffic signs, facilitating their movement across the highway.
- Small fauna tunnels allow safe passage for roe deer.
- Planting between Bovenbuurtweg and Landgoed Hoekelum, with a connection to the Edeseweg Viaduct, have been undertaken to support bats and their habitat.
- Roadside fencing is employed to avoid road kills.

- SolaRoad: Where Cycling Meets Solar Power
In Maartensdijk, Utrecht, the SolaRoad cycle path represents a groundbreaking project that combines cycling and solar panels on the road surface. This innovative approach not only maximizes energy efficiency but also minimizes the environmental impact of road infrastructure.

- Ecoduct Zwaluwenberg N417: Nature’s Overpass
Constructed over the A27 highway and a railway connecting Utrecht and Hilversum, the Ecoduct Zwaluwenberg N417 facilitates the safe passage of wildlife, including deer, badgers, pine martens, sand lizards, and studded blue beetles over busy transportation corridors. This impressive structure underscores the importance of coexisting with nature.

- N211 geeft energie: The CO2-Negative Road
The N211 geeft energie project between The Hague and Poeldijk, built from 2014 to 2018, sets a remarkable example by being the first CO2-negative road in the Netherlands. Through innovative energy extraction and sustainable construction practices, this road demonstrates how infrastructure can benefit both communities and the environment. Some exemplary green measures implemented on this road include:
- The road surface is designed to extract energy, which is then stored locally in a heat-cold storage system. Neighbouring companies are connected to the energy system, allowing for the exchange of heat, making it an efficient and sustainable energy source for the community
- Solar panels or cells are integrated into street lights, the roofs of bus shelters, and sight screens to generate electricity from renewable sources.
- The asphalt mixture used in construction is produced and processed at lower temperatures, reducing energy consumption during road production.
- The road surface is designed for maximum flatness for minimizing rolling resistance. This results in vehicles using less energy when traveling on the road to enhance energy efficiency.
- Wooden portals for traffic lights and bamboo signage are used as bio-based materials.
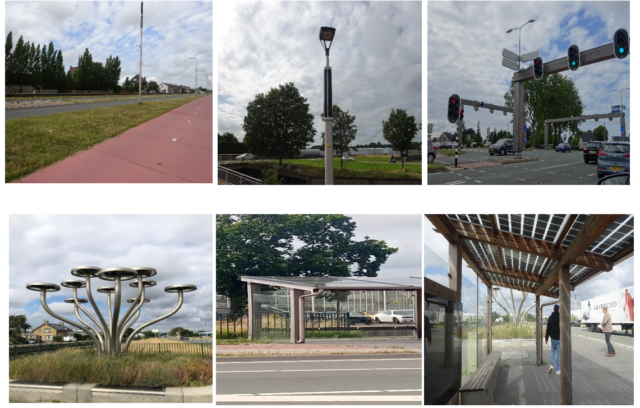

- A16 Rotterdam: ‘De Groene Boog’
The A16 Rotterdam project, known as ‘De Groene Boog,’ showcases a consortium’s collaborative efforts to create an environmentally friendly highway. With features like energy-generating infrastructure and wildlife conservation measures, it sets a new standard for sustainable road development. Some exemplary green measures implemented on this road include:
- The road and tunnel will generate the energy required for their maintenance through the use of solar panels. This project incorporates solar panels, LED lighting, electric transport, and hybrid equipment to minimize carbon emissions.
- During the construction of the tunnel in Lage Bergse Bos, green nets have been installed to guide bats safely across the construction sites.
- Construction activities that could disturb bird breeding were avoided during the breeding season, which spans from mid-March to mid-July.
- Fauna passages for hedgehogs will be constructed from Scheibroekse Park to Lage Bergse Bos.
- Noise pollution will be reduced by using additional noise-reducing asphalt on the A16 road surface and by implementing plant barriers.