By Farah Kamaleddine
Despite being home to the historic Euphrates and Tigris rivers, Iraq is facing severe water shortages affecting millions of people daily. Notwithstanding the high evapotranspiration water losses in Iraq, being a semi-arid country, climate change impacts concurrently with other challenges, including increasing and rapidly urbanizing populations, land and water degradation, and increased damage to infrastructure are exacerbating water shortage. The Anbar Governorate in particular is facing real water shortage problems characterized by a decrease in the water supply from the Euphrates River, particularly after the launch of the GAP project in Turkey, which consists of constructing around 22 dams (Shafaq, 2023). Anbar Governorate located in Western Iraq accounts for around 30% of Iraq’s total area making it one of the largest governorates in the country, and the traditional food basket of Iraq at the same time.
Being largely dependent on the Euphrates River, surface water is the major water resource for Anbar Governorate. With reduced inflow of transboundary water into the area, combined with expansion in agricultural area, it is crucial to examine changes in surface water sources, such as major reservoirs or lakes in the area. This serves into providing insights about the country’s strategic water reserves. Anbar’s key reservoirs such as Haditha reservoir and Al-Habbaniyah lake have seen a discernible decrease in water levels during the last four years. This decline can be attributed to reduced water inflows due to damming and excessive water abstraction in the upstream riparian states, especially Turkey and Iran, and the impact of climate change, including a significant reduction in rainfall coupled with escalating evaporation rates (Masoud et al., 2022). According to a recent commentary in “The Century Foundation”, satellite images utilizing the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) reveal that the Qadisiyah Lake, of strategic importance to Haditha Dam, has almost completely vanished.
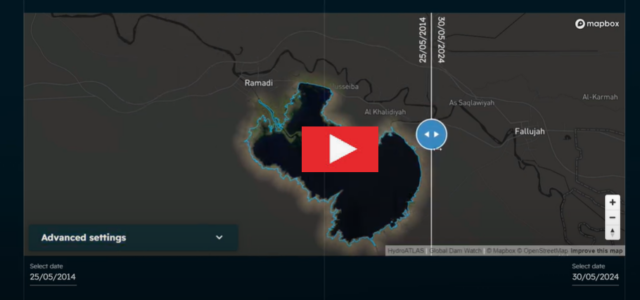
Using Global Water Watch and HydroATLAS database, a 10-year timelapse for the Al-Habbaniyah Lake was created for the period extending from May 2014 till May 2024. The timelapse shows a discernible decrease in water surface area of the lake, foreshadowing a real water crisis. Al- Habbaniyah Lake is a 140-square-kilometer man-made waterbody, located halfway between Ramadi and Al-Falluja, providing irrigation water. The observed decrease in water surface in this lake is coinciding with an expansion in center pivot agricultural production as reported in “The Century Foundation”. Not only this, but also a proliferation in artificial fishponds which have nearly doubled in recent years, discharge of untreated of partially treated wastewater, and mining activities, particularly for phosphorus which is very common in the area. Coming together, these challenges are causing a deterioration in surface water quality, including an increased risk of eutrophication which will be targeted in the upcoming blog post.
A video showing the 10-year timelapse for the Al-Habbaniyah could be viewed here:
The combined effect of prolonged droughts, warming temperatures, and dwindling water resources (both surface water and groundwater) is a critical challenge to agriculture in Anbar, and a serious threat to food security. It is driving an unenviable transformation in agricultural systems. Satellite images showed alarming temporal and spatial changes in major water lakes in Anbar Governorate, signifying the need for urgent control and remedy actions. Collective effort is needed to protect Anbar’s water resources from further dwindling, and to revive the agricultural system.
References:
Shafaq. 2023. Water crisis in southern Ramadi forces thousands to displace. Available: https://shafaq.com/en/Iraq/Water-crisis-in-southern-Ramadi-forces-thousands-to-displace.
Masoud, M., El Osta, M., Alqarawy, A., Elsayed, S. and Gad, M. 2022. Evaluation of groundwater quality for agricultural under different conditions using water quality indices, partial least squares regression models, and GIS approaches. Applied Water Science, 12, 244.
Subhi, H. (2023, September 01). “Satellite Monitoring Reveals the Startling Extent of Iraq’s Water Crisis”, The Century Foundation, https://tcf.org/content/commentary/satellite-monitoring-reveals-the-startling-extent-of-iraqs-water-crisis/